Decision Table Overview
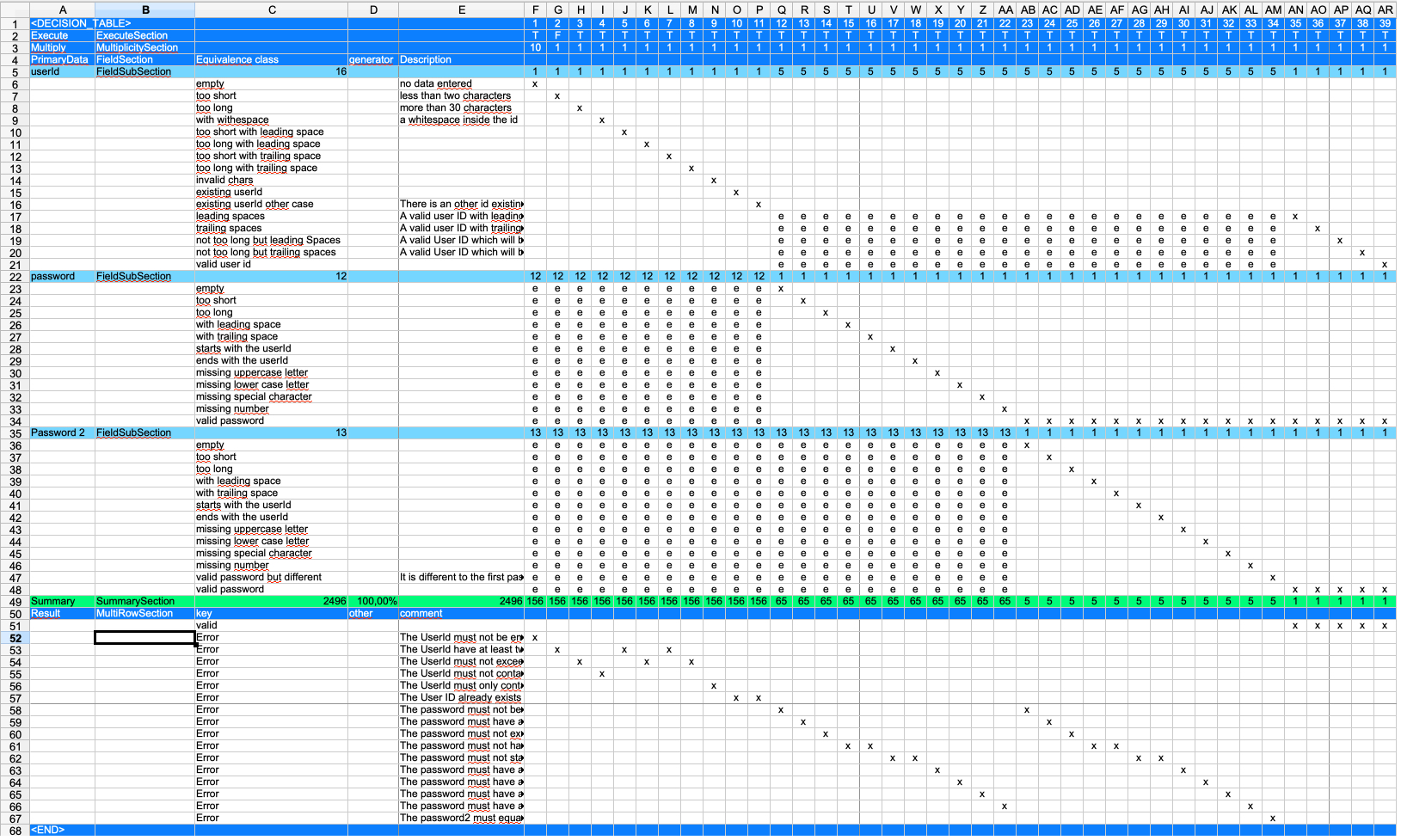
This figure shows an example of an equivalence class table. The column order is important. The first five columns are fixed. The test cases start with the 6th column. The parser finds the end of the test case by parsing the first row and searching for the first empty cell. So if you add an empty column in your table, the parser will stop there.
The table is divided into two sections: the right and the left of the red line.
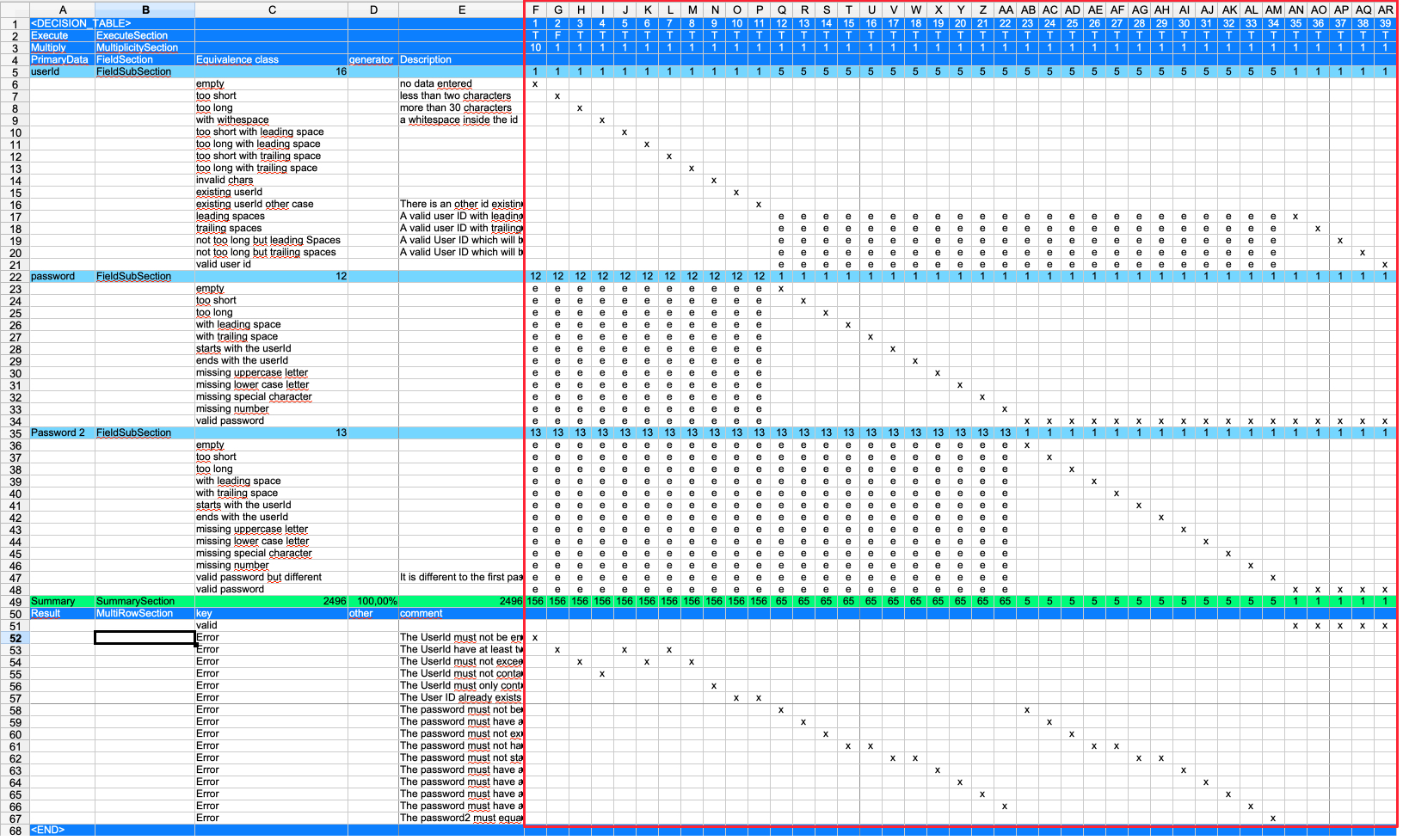
The right side shows the test cases. Each column on the right side is one test case. The column header of a test case is the name of this test case. In this example the name is just number. In column ''F'' we have the first test case - with the name ''1''.
The left side of the table deals with the fields, their descriptions and the expected result.
On the left, the ''Field Section'' is the primary data section. The primary data is the data that is directly manipulated in the test. But this is just a name. You can have as many 'FieldSection' elements as you like. A field section consists of one to multiple 'FieldSubSection' elements.
The field section describes the variety of data needed by the test. And therefore the number of tests to be created.
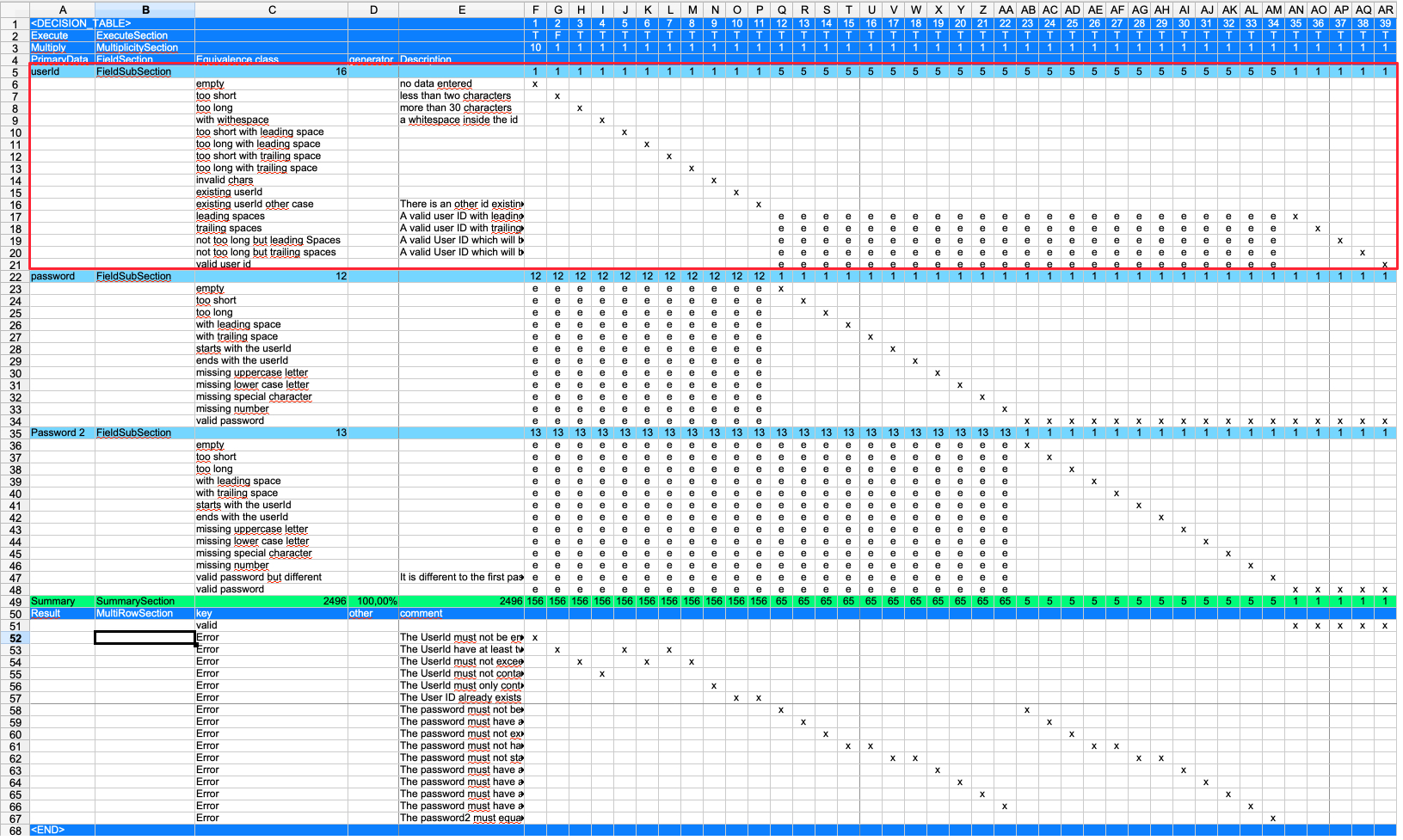
A subsection in this case is one field and all the equivalence classes for this field. An equivalence class defines the different kinds of field values with an equivalent behaviour.
For example: Let's say we have a field with a maximum length of 10 characters. Then all values entered with more than 10 chars will lead to an equivalent behaviour of the application. So it is not necessary to test with 11, 12, 13, … characters. The equivalence class is 'more than 10 chars'.
One fieldSection may have many fieldSubSections. The FieldSection groups fields together. Having one or multiple fieldSections has no impact on the table itself. All the fieldSubSections have to be combined.
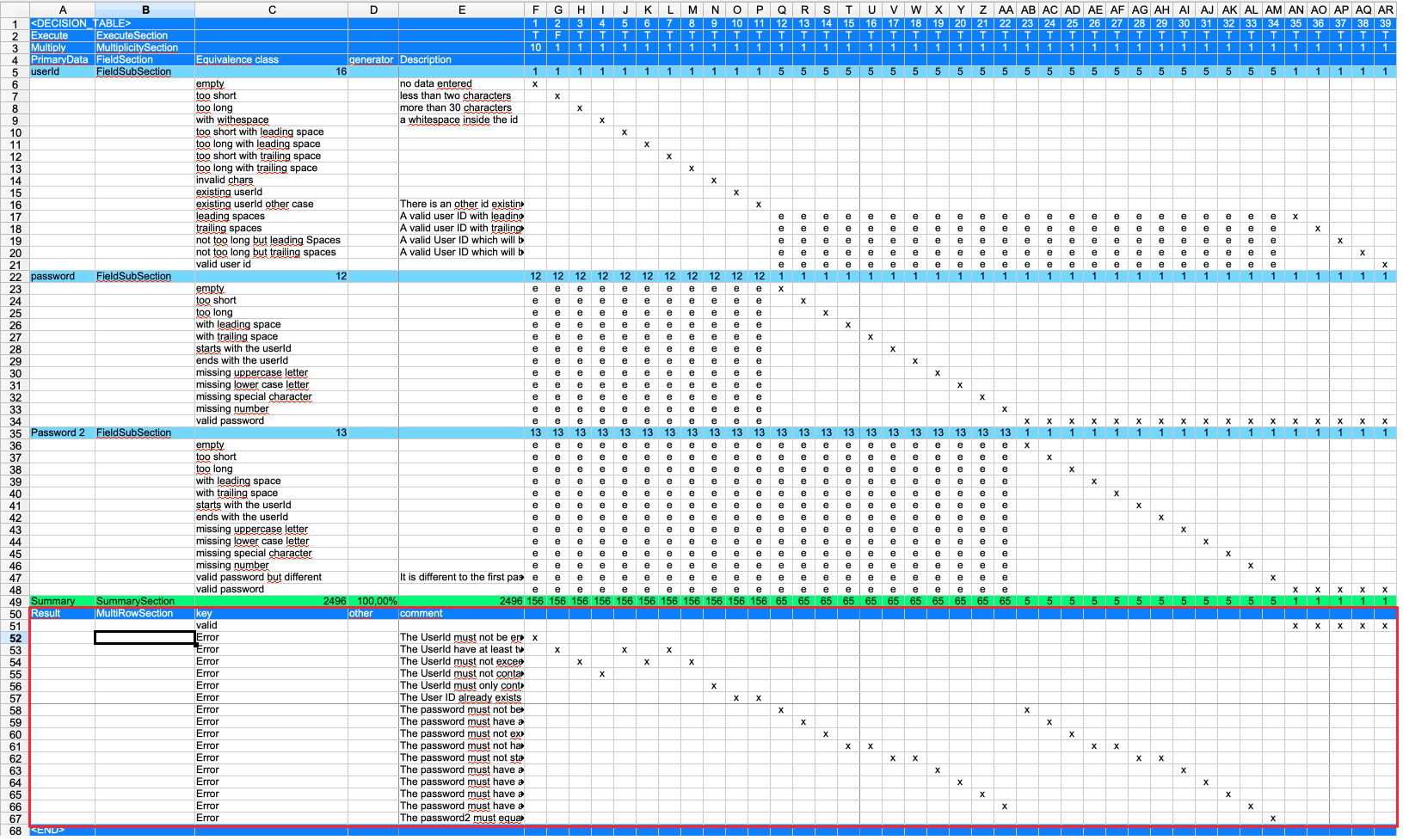
The multiple row sections can be used to describe the expected results or error messages. It is up to the user how many of these sections are in the table. It can also contain actions on the UI or other information needed.
